Excel Tips
Practical Excel help you can trust, fast. This hub collects our most useful Excel guides on formulas, calculations, formatting, PivotTables, templates, and advanced features, all written step by step with clear examples and screenshots. Whether you are learning Excel basics or doing complex data analysis on sales data, the goal is the same, accurate results without wasting time hunting through the ribbon.
If you already know what you need, use the site search to jump straight to the right tutorial. If you are not sure where to start, use the sections below.
Start here
Pick the path that matches what you are trying to do right now. If you are staring at a single cell wondering what to type, start with calculations and excel functions, type your formula, then press Enter to run it.
- Write a formula or fix a calculation
- Work faster with shortcuts and quick tricks
- Clean up formatting or build a chart
- Summarize data with PivotTables
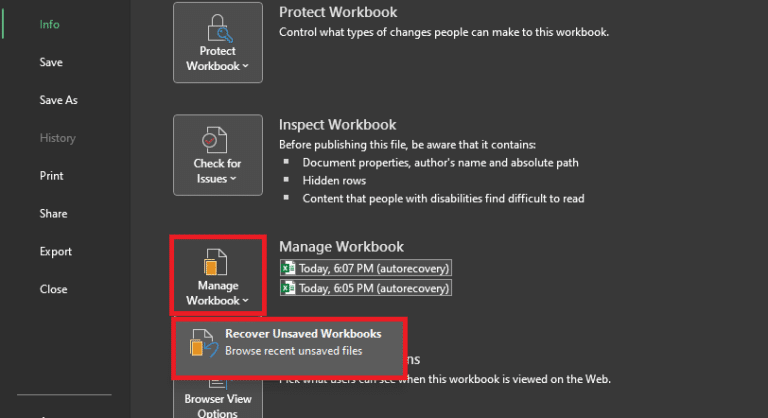
- Understand workbook basics and file handling
- Explore advanced features like Python in Excel
Excel workbook basics
An Excel workbook is the file, and it can contain multiple worksheets (tabs). If you collaborate with a team or move between devices, workbook basics matter as much as formulas. Getting the structure right also makes it easier to reuse a range of cells, keep column headers consistent, and avoid broken references later.
- Workbook vs worksheet, what changes when you copy or move sheets
- File types you will see most often, including .xlsx and .xls
- Safe sharing habits, like using clearly named versions and keeping source data separate from reports
- How to freeze panes so column headers stay visible while you scroll through data points
If you are downloading one of our templates into Excel, you will typically copy the sheet, then use File > Download and select the Excel option. Keep an eye out for feature differences if the template originated in Google Sheets. For workbooks that will be shared, keep number formatting consistent, especially commas for thousands in sales data, so readers interpret totals correctly.
Excel tricks and shortcuts
These guides are for speed, quality of life, and fewer clicks. If you work in Excel daily, shortcuts and small tricks usually deliver the biggest time savings. Many of the most-used commands live on the ribbon, but learning the keyboard equivalents is what makes Excel a powerful tool instead of a slow one.
- Excel keyboard shortcuts (including Windows Ctrl keys and Mac cmd shortcuts)
- Quick wins to learn next (paste special, fill handle habits, fast selection methods, freeze panes)
- Flash Fill tips for cleaning repeated patterns without writing formulas
- Calculate duration between dates with DATEDIF in Excel
- Comparing Excel files with Power Query
- Excel Macros (including when Visual Basic makes sense)
If you are not sure where a feature lives, check the Data tab for sorting, filtering, and refresh options, then use the ribbon search to jump to commands.
Excel calculations and formulas
We break down Excel formulas in a way that is easy to reuse. Every formula guide includes a syntactical breakdown, what each argument means, and what is optional. This approach helps you get accurate results, especially when you are running calculations across a large range of cells with thousands of data points.
Example syntax from our guide on IF contains partial text in Excel:
=IF(test, if-true, if-false)
From there, our tutorials walk through each argument with screenshots and real-world examples. If you are building calculations for workbooks that other people will maintain, this style helps you write excel functions that do not collapse later. In most cases, you will type the formula into a single cell, then press Enter, then copy it down the column if needed.
Popular formula and function guides:
- How to use the COUNTIF Excel function
- How to use the CHOOSE function in Excel
- How to use the NOT function in Excel
Common calculation problems, fast fixes
- If a formula returns #N/A, check whether a lookup value actually exists in your source range.
- If a formula returns #VALUE!, check for mixed data types, like text numbers that need conversion, or commas used inconsistently in imported numbers.
- If a formula returns 0 unexpectedly, confirm you are referencing the intended cells and not a blank range.
- If results look right but totals are wrong, confirm hidden rows, filters, and whether you are summing visible data only.
- If you are working with sales data, confirm your column headers match your assumptions, and that dates, currency, and IDs are stored consistently.
Excel formatting and data visualization
Formatting is where most spreadsheets either become readable or become a mess. We cover cleanup, table formatting, and practical dashboard design so your workbook stays usable. For quick scanning, visual tools like data bars can highlight the biggest data points without building a full chart.
Popular formatting and cleanup guides:
- How to remove dashes in Excel
- How to remove and edit table formatting in Excel
- How to swap cells
- How to find duplicates
If you are building a report, dashboards are usually the fastest way to turn raw data into decisions. We also cover graphs and charts, including how to keep labels readable and formats consistent as your workbook grows.
Excel pivot tables and data analysis
Pivot Tables are Excel’s fastest way to summarize large datasets without writing complex formulas. They are ideal when you need totals, counts, grouped summaries, or quick breakdowns by category, date, or owner. For complex data analysis, PivotTables often provide the cleanest route to accurate results, especially when you start with a well-structured range of cells and consistent column headers.
PivotTables, when to use them
- Use PivotTables when you need quick summaries and flexible slicing.
- Use formulas when you need row-level outputs that live beside your data.
- Use both when you want a PivotTable summary plus calculated fields outside the PivotTable for presentation.
PivotTables, common pitfalls
- Forgetting to refresh after source data changes (check the Data tab for Refresh All)
- Using a source range that does not include new rows, consider converting source data to a table first
- Date grouping behaving oddly when dates are stored as text
If your analysis involves frequent imports, cleanup, and repeatable transformations, you will often pair PivotTables with structured tables, consistent formatting, and clear column headers so your data points roll up correctly.
Advanced Excel, Python, and Copilot
Excel keeps evolving, and advanced features now overlap with analytics workflows that used to require separate tools. We publish guides and templates that reflect modern Excel use across desktop and cloud environments, from Power Query pipelines to Visual Basic automation when macros are still the simplest option.
One popular advanced topic is how to use Python in Excel. Python in Excel can unlock more advanced analysis inside the spreadsheet grid, but availability, compute limits, and licensing can vary by Microsoft 365 plan. If you are using Excel at work, confirm what your organization has enabled before you design a workflow around it.
Whether you need to modify a large dataset, audit formulas, build graphs, or clean up chart labels, our advanced Excel coverage is designed to be practical and repeatable.
Excel spreadsheet templates
Our team regularly creates spreadsheet templates that many readers use as Excel workbooks. A common workflow is to make a copy, then use File > Download and choose the Excel option.
This lets you start with a working structure instead of rebuilding from scratch. For example, you can use our financial planning templates, including budget templates, as a base and then adjust categories, formatting, calculations, and column headers to match your needs.
Note: if a template originated in Google Sheets, some features may behave differently in Excel depending on how the file was created and which Excel version you use.
A community of experts
We also publish tutorials and walkthroughs on YouTube, and we regularly respond to reader comments. If a guide helped you solve a real problem, share it with your team, and feel free to ask questions in the comments.
Excel tips FAQ
These quick answers cover the most common Excel questions readers ask, from workbook basics to PivotTables, formatting, and calculations.